How Can a Physiatrist Help Treat Your Pain?
YOU HAVE QUESTIONS? WE HAVE ANSWERS.
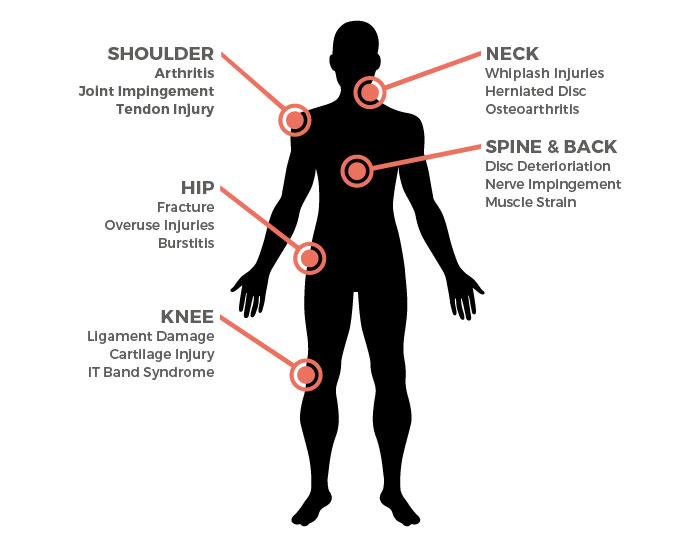
Arthritis is pain and stiffness in the joints. The most common cause is degenerative arthritis (called osteoarthritis), though there may be other causes like rheumatoid arthritis and gout.
Bursitis is inflammation of small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae that pad and lubricate joints. Bursitis may be the result of overuse, acute injury or other conditions.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, behavior, gender (women are more likely to suffer from the condition), and overall physical health (being overweight is a major risk factor).
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Chronic pain can range from mild to excruciating, and can involve any part of the body. The pain may be shooting, burning, aching, stabbing or electrical, and may involve stiffness and loss of mobility. There are many causes, which vary from acute injury to osteoarthritis and disorders of the nervous system.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Degenerative Disc Disease isn’t actually a disease, but rather pain stemming from the gradual breakdown of one or more of the cushioning discs in the spine. Though the term “degenerative” can be alarming, it doesn’t mean the condition keeps getting worse. In fact, the pain from the condition usually improves over time—especially with treatment.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, lumbar discography, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Elbow pain can stem from a variety of acute and chronic conditions, including: bursitis, tendonitis, overuse, arthritis and trauma.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Golfer’s elbow is similar to tennis elbow (and can be experienced by anyone—not just golfers. It occurs when the tendons that connect the forearm muscle to the bony bump inside the elbow become inflamed through overuse—usually from activities that involve clenching the hand.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
A herniated disc occurs when the jelly-like fluid within the cushioning discs of the spine is pressed out through a crack or rupture of the disc. This puts pressure on the nerves within the spinal column, causing pain.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Knee pain can be caused by a number of different injuries and conditions, but some of the most common are: arthritis, tendon and/or ligament injury, overuse, lifestyle and complications from injuries to other parts of the leg.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Leg pain has a number of causes, both chronic and acute. Most pain is caused by acute injury or overuse, but more serious causes can include nerve impingement, spinal degeneration, neuropathy, and autoimmune disorders.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Lower back pain has a number of causes, ranging from pressure on the nerves in the back to muscle strain. The majority of lower back pain can be treated without surgery through minimally invasive procedures.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Muscle pain is usually caused by overexertion. Some pain is natural after strenuous activity, but more severe pain can indicate a greater problem, like a tear in the muscle tissue.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, medication, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Myofascial pain syndrome is a chronic condition in which pressure on a trigger point causes pain in another, seemingly unrelated area of the body. It commonly occurs after a muscle has been repeatedly contracted, often due to a job-, sport- or hobby-related activity.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, medication, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Neck pain can be mild or severe and generally involves muscle pain, trauma, or a condition in which a structure within the neck puts pressure on the surrounding nerves.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
There many causes for nerve pain—some minor, some serious. It’s important to see your doctor for treatment if any burning or electric pain persists for more than a few days.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Neuropathy is a common affliction that usually manifests as a complication of another condition, like injury, exposure to certain toxins or drugs, including chemotherapy, infections and diabetes. It can affect autonomic, motor and/or sensory nerves and is often experienced as a tingling, burning, pins-and-needles pain in the affected nerve.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
The body naturally loses bone density over time, but a variety of factors can combine to cause some people to lose bone mass at a faster rate. This can result in frequent fractures and injuries like vertebral collapse.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
The goal of treatment after surgery is to speed recovery, mitigate the chance of complications, and restore as much function as possible. In general, the more invasive the procedure, the more involved the recovery will be.
Treatments may include: Physical therapy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Rehabilitation after a traumatic injury or attack—especially one that affects the brain—can be exceptionally difficult. Dedicated and consistent treatment is key to restoring the maximum quality of life to the patient as quickly as possible.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical, vocational and behavioral therapy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment, medication.
Repeatedly overusing a muscle or joint in your body—either during a single event or over a long time—can cause inflammation or damage to the underlying tissue, which leads to pain.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, trigger-point injections, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Rotator cuff injuries often occur in people who repeatedly make overhand motions with their arms (usually during sporting, hobby or work activities) and can cause pain, loss of motion, or even frequent dislocation of the shoulder. Strengthening the joint can often resolve the problem without the requirement for surgery.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a condition that affects the sacroiliac (SI) joint between the spine and the hips. Either the joint is moving too much or too little, which causes pain that radiates to other body structures.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, intra-articular joint injections, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Sciatica is pain in the sciatic nerve that runs from the lower back into the legs. It isn’t a medical diagnosis in-and-of itself, but rather a term to describe the pain caused by pressure or damage to the nerve from an external source.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Scoliosis can be inherited or caused by another condition, including trauma, degeneration of the spinal column and muscle and nerve disorders. Because the spine isn’t in the correct position, scoliosis can result in pain and loss of mobility.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Spinal injury can result from an acute trauma (like a sports injury) or from chronic conditions (such as osteoporosis). Because the spinal column sends signals from the brain to all of the body’s muscles, an injury to those nerves can often require extensive rehabilitation.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injectionsmedial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal—the empty space through which the nerves of the spinal column extend at the base of the spine. This can put pressure on the nerves and cause shooting, burning pain in the legs, abdomen and lower back.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, gangliar impar nerve blocks, lumbar discography, alternativetherapies, behavioral adjustment.
Tendonitis refers to inflammation of one or more tendons (tough, fibrous tissue that connects muscle to bone). This is often a result of overuse or acute injury—and, while painful—tendonitis can usually be treated without surgery.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
Tennis Elbow is inflammation of the tendons in the elbow, generally as a result of overuse of the joint. You don’t have to be a tennis player to be affected, but a motion like swinging a tennis racket can eventually cause irritation and severe pain. See “Golfer’s Elbow.”
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, intra-articular joint injections, medication, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
There are many causes of upper back pain, ranging from degenerative arthritis to muscle strain. Most simple issues can be treated non-surgically. See lower back pain.
Non-surgical treatments may include: Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, intra-articular joint injections, medial branch nerve blocks, medication, radiofrequency neurotomy, alternative therapies, behavioral adjustment.
The road to a faster, fuller recovery starts here.
Meet a few of our featured providers today.

Comments are closed.